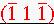 .
.Homework Set 5
Solutions
These questions relate to the close packed sphere model of the face-centered cubic lattice. This model is constructed of two sets of (111) planes each consisting of 6 spheres arranged in an equilateral triangle. On the first set the atoms are labeled with letters B through G and on the second set they are labeled H through M. There are two single spheres labeled A and N. The two sets of 6 spheres are stacked on top of each other so that the spheres of one set are nestled into the hollows between the spheres of the other set. The sphere A is placed on top of the first set of 6 atoms and the sphere N is placed behind the second set to form a face-centered cubic structure.Fix a coordinate system such that the center of sphere H is the origin and a line through the centers of spheres H and E is the x axis, a line through H and N is the y axis and the z axis lies through H and F.
1. What are the direction indices of the vector BG (consider BG as short hand notation for the vector from the center of sphere B to sphere G)?
Answer: Subtract coordinates of B from coordinates of G
2. What are the direction indices of vector BC?
Answer: [0 1 1]
3. Determine the miller indices of the plane containing BG and BC.
Answer:
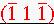 .
.4. Determine the direction indices of the normal to the plane containing BG and BC.
Answer:
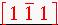 . Note that these indices are all the same integers as the miller indices of the plane containing the two vectors but are all the negatives of the miller indices. Of course if the position of the two planes in the scheme of taking cross products had been interchanged then we would get the set of direction indices that are the negatives of the set that we obtained above. Either answer is correct for most purposes. Special Note: this procedure only works for cubic crystals.
. Note that these indices are all the same integers as the miller indices of the plane containing the two vectors but are all the negatives of the miller indices. Of course if the position of the two planes in the scheme of taking cross products had been interchanged then we would get the set of direction indices that are the negatives of the set that we obtained above. Either answer is correct for most purposes. Special Note: this procedure only works for cubic crystals.5. Locate a tetrahedral interstitial position by giving the letters of the labels of 4 spheres located at the corners of the tetrahedron and also the coordinates of the center of the tetrahedron with respect to the fixed coordinate system.
Answer: It helps to have the hard sphere model to answer this question since we need to find 4 spheres that are contacting each other to define the corners of the tetrahedron. In the drawing we can locate B, D and C that are all in contact in the close-packed plane and then A is in contact with all three of these spheres. We see that all the distances between two of these spheres are equal to 1/2 of a body diagonal of the cube. Therefore the center of the tetrahedron lies at 3/4, 1/4 , 3/4.
6.Locate an octahedral interstitial position by giving the letters of the labels of 6 spheres located at the corners of the octahedron and also the coordinates of the center of the octahedron with respect to the fixed coordinate system.
Answer: An octahedron has eight faces and six corners. It looks like two four sided pyramids stacked base to base. In the FCC structure we can find an octahedran by taking all the atoms in the centers of the side faces and connecting them to form a square. Then connect each of the corner atoms of this square to the atoms at the centers of the top and bottom faces. Thus an answer is K, B, L, M, D and C. These can be arranged in any order. The coordinates of the center of the octahedron are obviously 1/2, 1/2, 1/2 .
7. Give the position coordinates of all the tetrahedral interstitial positions in the unit cell.
Answer: The tetrahedron described above in problem 5 can be thought of as inscribed in a cube which is 1/8 of the volume of the unit cube. There are eight similar subcubes in the unit cube and each is the center of a similar tetrahedron. The complete set of coordinates is thus ( 1/4, 1/4, 1/4 );( 3/4, 1/4, 1/4 );( 1/4, 3/4, 1/4 ) ( 1/4, 1/4, 3/4 );( 3/4, 3/4, 1/4 );( 3/4, 1/4, 3/4 );( 1/4, 3/4, 3/4); (3/4, 3/4, 3/4).
8. Determine the miller indices of the plane passing through the centers of the spheres I, B, and D.
Answer: We can solve this problem by two different ways, either imagine extending the plane to find its point of intersection with the axes or find the direction indices of the two vectors and take the cross products. Take H as the origin of axes. BI = 0-1/2, 1-0, 1-1/2 = -1/2, 1, so
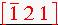 . DI =
. DI =
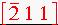 Thus BIxDI is:
Thus BIxDI is:
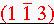 .
.The following questions pertain to the hard sphere model of the hexagonal close-packed structure.Take the unit cell axes to be the vectors AB, AC, and AK.
9. What are the coordinates of the center of the sphere H with respect to the unit cell axes defined above?
Answer: Sphere H lies directly above the centroid of the euilateral triangle formed by spheres A, B and D. Remeber that the coordinates of a point are given in terms of fractional values of the corresponding unit cell axes which are not all orthogonal in this case. Thus the coordinates are (2/3, 1/3, 1/2).
10. Determine the direction indices of the following vectors:
Answer: AB = [1 0 0], AD = [1 1 0], AL = [1 0 1], AN = [1 1 1]
11. Determine the miller indices of the planes BLND, BLMC,BKC (Where plane is defined by passing through points located at centers of the labeled spheres).
Answer: BLND = (1 0 0), BLMC = (1 1 0), BKC = (1 1 1)
12. Locate a tetrahedral interstitial position by giving the letters of the labels of 4 spheres located at the corners of the tetrahedron and also the coordinates of the center of the tetrahedron with respect to the fixed coordinate system.
Answer: A, B, D, H coordinates of center (2/3, 1/3, 1/8)
The figures show the geometry of the tetrahedron to assist in locating its center in coordinate space fixed to the hexagonal unit cell axes. The first figure shows a plan view of the tetrahedron. The second figure is an elevation view. The following two figures show the equilateral triangle that forms the base of the tetrahedron with lables to help with the discussion. The side of the equilateral triangle is equal to the a parameter of the hcp crystal. Obviously a = 2r, where r is the atomic radius. The triangle 123 is an isoceles triangles with two sides b in length. The triangle 345 is similar with two sides u in length. Since side 45 of this triangle is a/2 in length, it follows that u = b/2 and that b is 2/3h where h is the height of the equilateral triangle. In the 4th figure a line 36 has been added (point 3 is at the position indicated in the 3rd figure, but has been omitted for clarity). This line is parallel to the line 14 and it is then obvious that the length of line 26 is 2a/3 and since 163 is an isoceles triangle line 63 has a length of 1a/3. Also line 63 is parallel to the b axis of the unit cell therefore the first two coordinates are 2/3, 1/3. It remains to find the third coordinate. Looking at the 2nd figure we see a right triangle with hypotenuse 2r = a and one side b and the third side y in length. From the 3rd figure we can find the value of
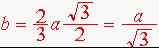 . Therefore
. Therefore
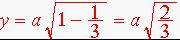 From similar triangles in the second figure we see that z/r = 2r/y. Thus
From similar triangles in the second figure we see that z/r = 2r/y. Thus
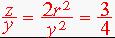 . Now y = c/2 where c is the lattice parameter of the hexagonal unit cell. Finally we find z = 3c/8 , but the position coordinate in the c direction is y - z =1/8.
. Now y = c/2 where c is the lattice parameter of the hexagonal unit cell. Finally we find z = 3c/8 , but the position coordinate in the c direction is y - z =1/8.
13.Locate an octahedral interstitial position by giving the letters of the labels of 6 spheres located at the corners of the octahedron and also the coordinates of the center of the octahedron with respect to the fixed coordinate system.
Answer: This is extremely difficult without having the hard sphere model to play with. The arrangement of atoms must be similar to the arrangement of atoms in the octahedron of the fcc structure. To form the base we need four atoms that form a square such as IHLP then the two capstone atoms such as K and an atom in the plane of IJH but in the adjacent unit cell Let's call it R (as in "r" you there?). Then the answer is KIHLPR coordinates of center (1/3,-1/3,3/4) .
