|
General
Interests
Current Research
Projects
Selected Publications
Courses
Turbulence and Sediment
Modeling
Laboratory
|
General
Interests
My
research interest is in landscape mechanics with a primary focus
on fluvial geomorphology, sediment transport, and surface water
processes.
Current
Research Projects
I am developing a set of LES and hybrid techniques for turbulence
in environmental flows. Sediment transport is then calculated
using the LES results either by bedload calculations from the
temporally- and spatially- varying bed stress, or by 3D
advection-diffusion modeling of suspended sediment.
I am building a suite of environmental morphodynamic models
involving 3D steady RANS calculations for environmental flows. At
each time step sediment continuity is solved and the 3D
structured or unstructured grid is adjusted accordingly. This
modeling system is being developed for simulation of bar growth
in rivers and large-scale erosion and deposition of eolian
landscapes.
I am conducting numerical simulations of turbulence and sediment
transport by combining turbulence-resolving LES simulations with
particle-resolving distinct element method (DEM) modeling of each
sediment particle. Using this method I directly calculate the
motion of bedload and suspended load grains, thus relying on no
empirical parameterizations of sediment fluxes. I am testing the
model with previous experimental work. My colleagues and I have
designed a series of flume experiments to test the validity of
the spatial and temporal distribution of transport predicted by
the simulations.
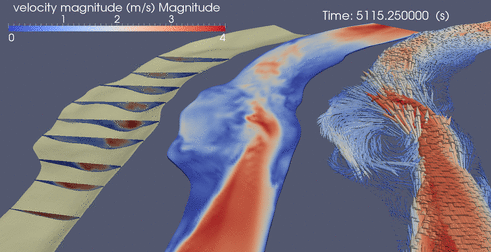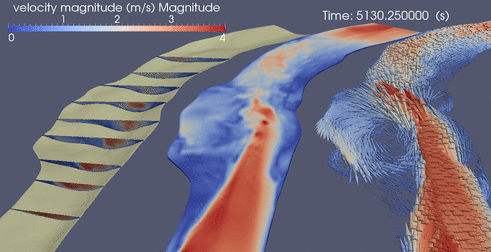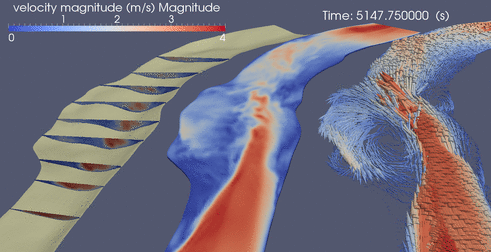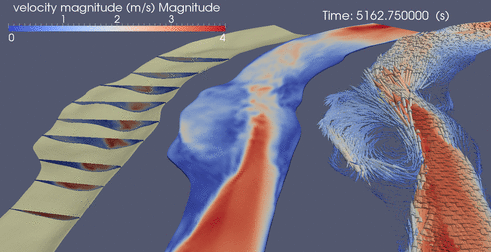
Below are a few random clips of various simulations
|
|
|
|
DES of Grand Canyon Eddy
|
|
|
|
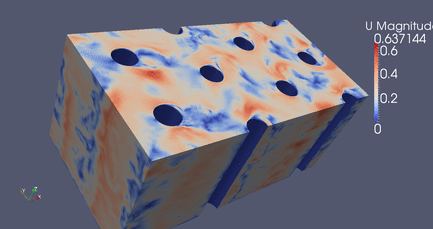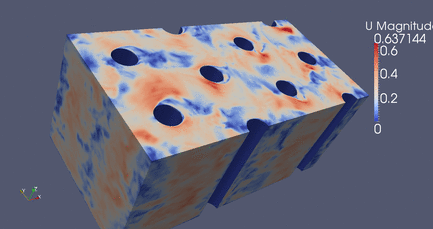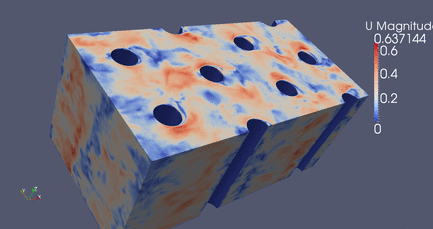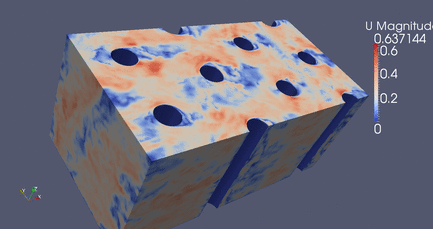
|
|
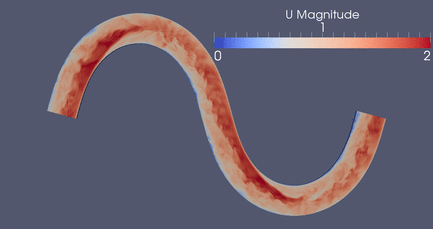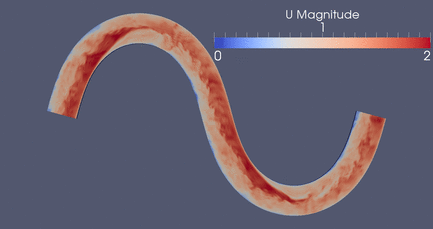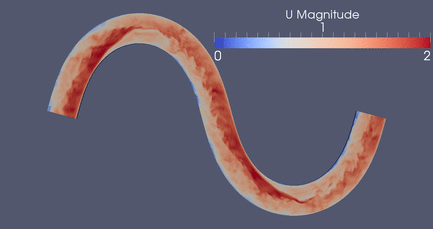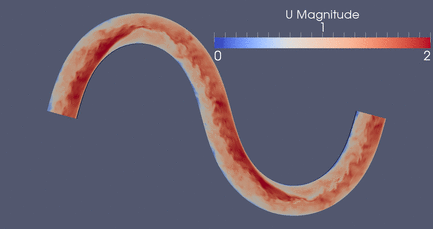
DES Meander , 3D RANS, 2D Depth-Averaged Flow Models
Click
Here for a high resolution version if this meandering
simulation
|
DES Flow Through Cylinders
Click Here
for high resolution version
|
|
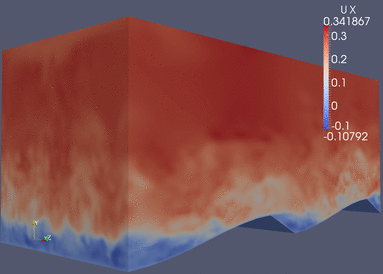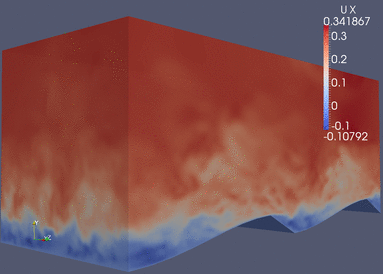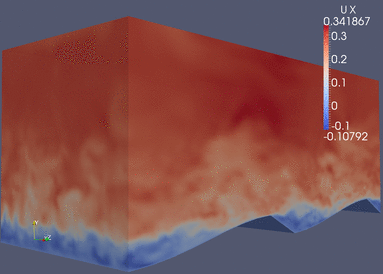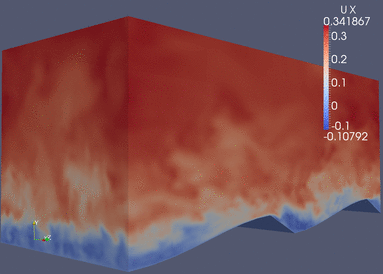
|
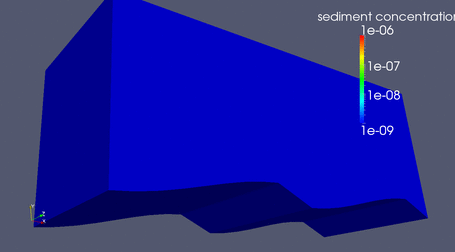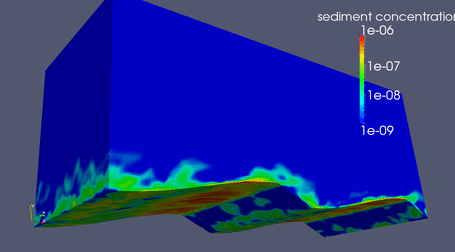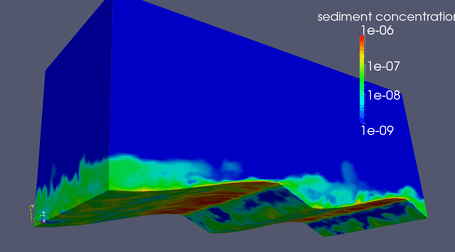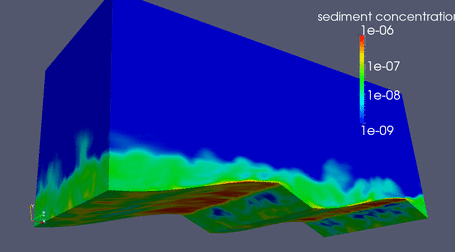
|
|
DES over ripples
|
Suspended Sediment over Ripples driven by DES
|
|
|
|
|
LES over a flat bed
|
Suspended Sediment driven by LES flow over flat bed
|
Publications
Schmeeckle,
M.W. (2014). The role of velocity, pressure, and bed stress
fluctuations in bed load transport over bed forms: numerical
simulation downstream of a backward facing step. Earth Surface
Dynamics Discussions. , 2, 715-732,
doi:10.5194/esurfd-2-715-2014.
Figure
1 animation , Figure
5 animation
Schmeeckle,
M.W. (2014). Numerical simulation of turbulence and sediment
transport of medium sand. Journal of
Geophysical Research: Earth Surface. doi: 10.1002/2013JF002911
Larson,
P., R.I. Dorn, R.I., R.E. Palmer, Z. Bowles, E. Harrison, S.
Kelley, M.W.
Schmeeckle,
and J Douglass (2014) Basin and Range Hydrological Integration
and Pediment Evolution in the Southwestern USA, Physical
Geography. doi: 10.1080/02723646.2014.931089
Yager,
E. M., & Schmeeckle, M. W. (2013). The influence of
vegetation on turbulence and bedload transport and bedload
transport. Journal of Geophysical
Research: Earth Surface.
Furbish,
D. J., & Schmeeckle, M. W. (2013). A probabilistic derivation
of the exponential-like distribution of bed-load particle
velocities. Water Resources
Research,
Alvarez,
L., & Schmeeckle, M. (2013). Erosion of river sandbars by
diurnal stage fluctuations in the colorado river in the marble
and grand canyons: Full-scale laboratory experiments.
River Research and Applications,
Furbish,
D. J., Ball, A. E., & Schmeeckle, M. W. (2012). A
probabilistic description of the bed load sediment flux: 4.
fickian diffusion at low transport rates. Journal
of Geophysical Research, 117(F3),
F03034.
Furbish,
D. J., Haff, P. K., Roseberry, J. C., & Schmeeckle, M. W.
(2012). A probabilistic description of the bed load sediment
flux: 1. theory. Journal of
Geophysical Research, 117(F3),
F03031.
Furbish,
D. J., Roseberry, J. C., & Schmeeckle, M. W. (2012). A
probabilistic description of the bed load sediment flux: 3. the
particle velocity distribution and the diffusive flux.
Journal of Geophysical Research, 117(F3),
F03033.
Roseberry,
J. C., Schmeeckle, M. W., & Furbish, D. J. (2012). A
probabilistic description of the bed load sediment flux: 2.
particle activity and motions. Journal
of Geophysical Research, 117(F3),
F03032.
Travis,
Q. B., Schmeeckle, M. W., & Sebert, D. M. (2010).
Meta-analysis of 301 slope failure calculations. I: Database
description. Journal of Geotechnical
and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 137(5),
453-470.
Travis,
Q. B., Schmeeckle, M. W., & Sebert, D. M. (2010).
Meta-analysis of 301 slope failure calculations. II: Database
analysis. Journal of Geotechnical
and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 137(5),
471-482.
Douglass,
J., Meek, N., Dorn, R. I., & Schmeeckle, M. W. (2009). A
criteria-based methodology for determining the mechanism of
transverse drainage development, with application to the
southwestern united states. Geological
Society of America Bulletin, 121(3-4),
586-598.
Furbish,
D. J., Childs, E. M., Haff, P. K., & Schmeeckle, M. W.
(2009). Rain splash of soil grains as a stochastic
advection-dispersion process, with implications for desert
plant-soil interactions and land-surface evolution.
Journal of Geophysical Research, 114,
F00A03.
Travis,
Q. B., Houston, S. L., Marinho, F. A. M., & Schmeeckle, M.
(2009). Unsaturated infinite slope stability considering surface
flux conditions. Journal of
Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 136(7),
963-974.
Akahori,
R., Schmeeckle, M., & Ikeda, S. (2008). Numerical calculation
of suspended sediment transport by using a particle-based method.
Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Japan,
57, 449-460.
Akahori,
R., Schmeeckle, M. W., Topping, D. J., & Melis, T. S. (2008).
Erosion properties of cohesive sediments in the colorado river in
grand canyon. River Research and
Applications, 24(8), 1160-1174.
Fernando,
H. J., Voropayev, S. I., & Schmeeckle, M. W. (2008). Ripple
dynamics and benthic transformations under variable wave forcing.
().DTIC Document.
Furbish,
D. J., Schmeeckle, M. W., & Roering, J. J. (2008). Thermal
and force-chain effects in an experimental, sloping granular
shear flow. Earth Surface Processes
and Landforms, 33(13), 2108-2117.
Douglass,
J., & Schmeeckle, M. (2007). Analogue modeling of transverse
drainage mechanisms. Geomorphology,
84(1), 22-43.
Furbish,
D. J., Hamner, K. K., Schmeeckle, M., Borosund, M. N., &
Mudd, S. M. (2007). Rain splash of dry sand revealed by
high-speed imaging and sticky paper splash targets.
J.Geophys.Res, 112(F01001),
F01001.
Schmeeckle,
M. W., Nelson, J. M., & Shreve, R. L. (2007). Forces on
stationary particles in near-bed turbulent flows. Journal
of Geophysical Research, 112(F2),
F02003.
Nelson,
J., Burman, A., Shimizu, Y., McLean, S., Shreve, R., &
Schmeeckle, M. (2006). Computing flow and sediment transport over
bedforms. River, Coastal and
Estuarine Morphodynamics: London, Taylor \& Francis Group, ,
861-872.
Akahori,
R., & Schmeeckle, M. (2005). Numerical analysis of
secondary-flow around a spur dike using a three-dimensional free
water surface LES model. Proceedings
of the 4th IAHR Symposium on River, Coastal, and Estuarine
Morphodynamics, , 921-930.
Mango,
A. J., Schmeeckle, M. W., & Furbish, D. J. (2004). Tidally
induced groundwater circulation in an unconfined coastal aquifer
modeled with a hele-shaw cell. Geology,
32(3), 233-236.
Schmeeckle,
M. W., & Nelson, J. M. (2003). Direct numerical simulation of
bedload transport using a local, dynamic boundary condition.
Sedimentology, 50(2),
279-301.
Nelson,
J. M., Schmeeckle, M. W., Shreve, R. L., & McLean, S. R.
(2001). Sediment entrainment and transport in complex flows.
River, Coastal and Estuarine
Morphodynamics, , 11-35.
Schmeeckle,
M. W., Nelson, J. M., Pitlick, J., & Bennett, J. P. (2001).
Interparticle collision of natural sediment grains in water.
Water Resources Research, 37(9),
2377-2391.
Shimizu,
Y., Schmeeckle, M., & Nelson, J. (2001). Direct numerical
simulation of turbulence over two-dimensional dunes using CIP
method. Journal of Hydroscience and
Hydraulic Engineering, 19(2),
85-92.
Nelson,
J. M., Schmeeckle, M. W., & Shreve, R. L. (2000). Turbulence
and particle entrainment. Gravel-Bed
Rivers,
Schmeeckle,
M. W. (1999). A dynamic boundary condition for bedload sediment
transport in non-uniform, hydraulically rough turbulent boundary
layers. Annual Journal of Hydraulic
Engineering, Japan Society of Civil Engineers, 42,
653-658.
Schmeeckle,
M. W., Shimizu, Y., Baba, H., & Ikezaki, S. (1999). Numerical
and experimental investigation of turbulence over dunes in
open-channel flow. Monthly Report of
the Civil Engineering Research Institute, 551,
2-15.
Schmeeckle,
M., Shimizu, Y., Hoshi, K., Baba, H., & Ikezaki, S. (1999).
Turbulent structures and suspended sediment over two-dimensional
dunes. River, Coastal and Estuarine
Morphodynamics, Proceedings International Association for
Hydraulic Research Symposium, ,
261-270.
Shimizu,
Y., Schmeeckle, M., Hoshi, K., & Tateya, K. (1999). Numerical
simulation of turbulence over two-dimensional dunes.
River, Coastal and Estuarine
Morphodynamics, Proceedings International Association for
Hydraulic Research Symposium, ,
251-260.
Schmeeckle, M. W.
(1998). The mechanics of bedload sediment transport.
Animations
|
|