Research Highlights
Photon & dilepton emission from magnetized QGP
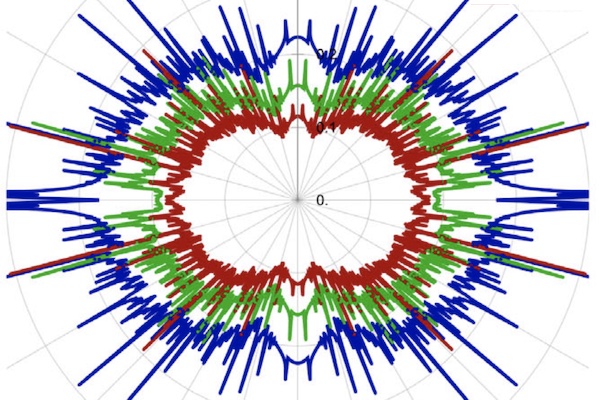
Description: Photon & dilepton emission rates & profiles carry a great deal of information about the plasma emitting them. In particular, these electromagnetic probes can tell about the presence of a background magnetic field.
Representative papers: [1] Ellipticity of photon emission..., [2] Photon polarization tensor..., [3] Nonzero baryon density..., [4] Dilepton production..., [5] Photon and dilepton emission anisotropy...
Chiral hydrodynamics
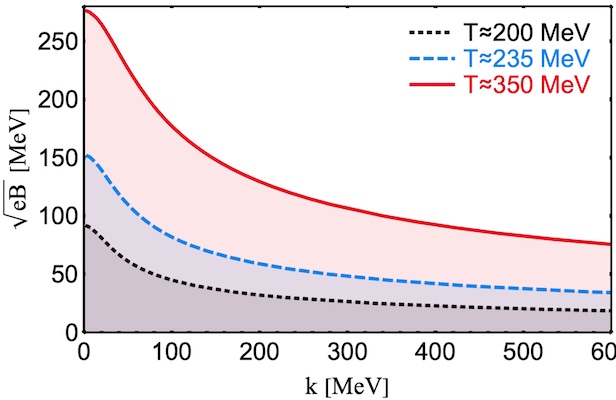
Description: Chiral hydrodynamics describes dynamics of chiral plasmas at large distance and long times. Collective modes in chiral hydrodynamics may have unusual features.
Representative papers: [1] Hydrodynamic modes..., [2] Second-order dissipative hydrodynamics..., [3] Overdamped chiral magnetic wave...
Chiral anomalous effects
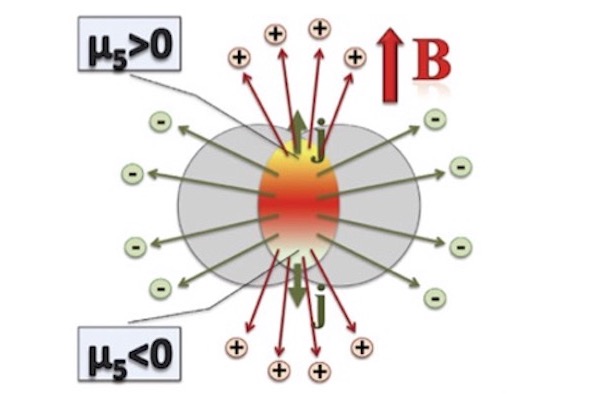
Description: Chiral magnetic and chiral separation effects are just two examples of quantum anomalous phenomena with macroscopic consequences in (quasi-)relativistic plasmas.
Representative papers: [1] Radiative corrections..., [2] Chiral effects in a slab..., [3] Anomalous Maxwell equations..., [4] Normal ground state...
Topological semimetals
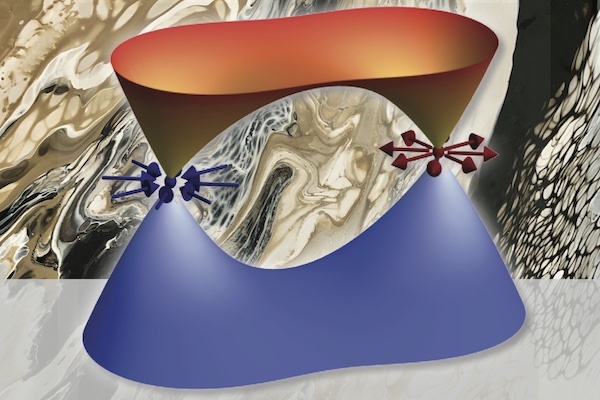

Description: Two examples of topological materials are Dirac and Weyl semimetals with massless electron quasiparticles. They are three-dimensional analogs of graphene.
Representative papers: [1] Chiral anomaly, dimensional reduction, and magnetoresistivity..., [2] Anomalous transport properties..., [3] Dirac semimetals A3Bi..., [4] Consistent Chiral Kinetic Theory..., [5] Origin of dissipative Fermi arc...
Graphene
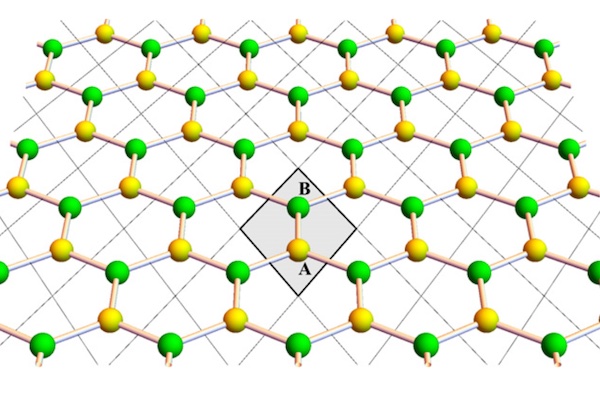
Description: Graphene is a two-dimensional Dirac semimetal with massless electron quasiparticles, described by the Dirac equation. In a sufficiently strong magnetic field, quasiparticles become massive (sometimes called the anomalous quantum Hall effect). The phenomenon is similar to magnetic catalysis in relativistic models.
Representative papers: [1] Quantum field theory in a magnetic field..., [2] Dynamics in the quantum Hall effect..., [3] Excitonic gap, phase transition..., [4] Magnetic field driven metal-insulator phase transition...
Color superconductivity
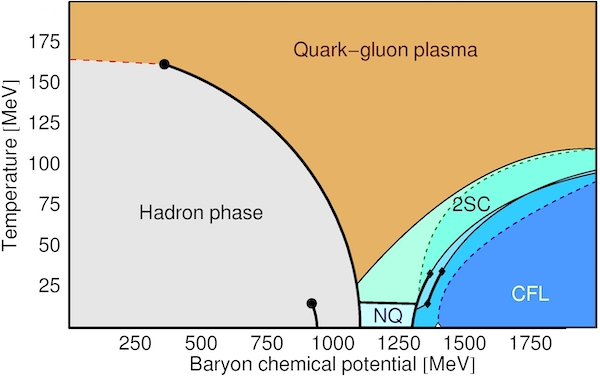
Description: Color superconductivity is analogous to low-temperature superconductivity in metals but occurs in dense quark matter. Such states of matter may appear in the central regions of compact stars.
Representative papers: [1] Two Lectures on Color Superconductivity, [2] Chromomagnetic instability..., [3] Gapless two-flavor color superconductor, [4] Schwinger-Dyson Approach...
Magnetic catalysis
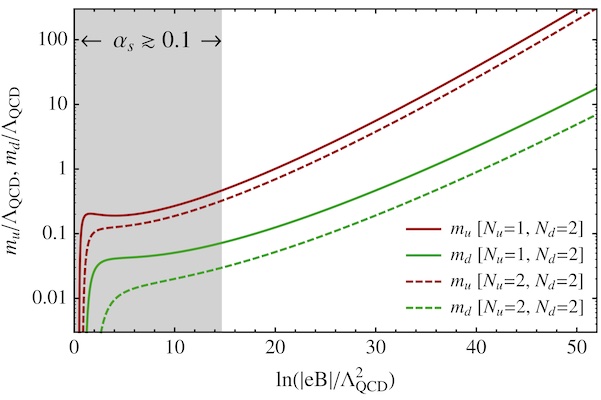
Description: In quantum field theory, enhancement of spontaneous chiral symmetry breaking by an external magnetic field is called magnetic catalysis. As a consequence, massless particles acquire a mass.
Representative papers: [1] Quantum field theory in a magnetic field..., [2] Magnetic Catalysis: A Review, [3] Magnetic catalysis in QCD.., [4] Theory of the Magnetic Catalysis..., [5] Catalysis of Dynamical Flavor Symmetry Breaking ...